About Bonds
A bond is a loan or purchase that the bond holder makes to the issuer. Bonds can be issued by governments, corporations or bodies that are looking to raise capital. When you trade a bond, you are taking a position on the price of the underlying instrument and not purchasing the instrument itself. This means that if you feel the bond your trading will increase in value, you would take a long position and if you feel the value of the bond would decrease, you would take a short position.
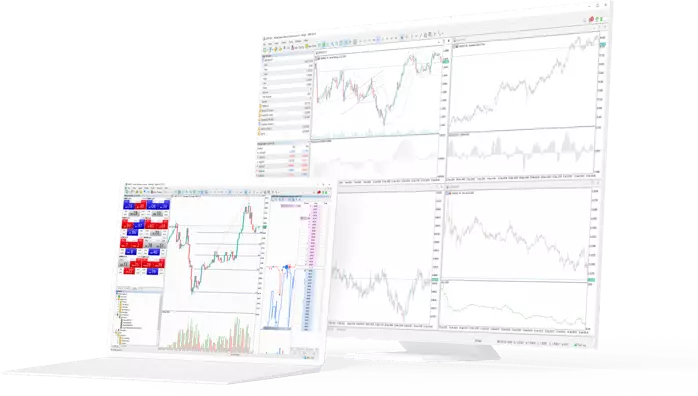
A Safer Haven for Your Money
Explore the least volatile market with competitive spread
3 world’s most traded bonds - Euro Bund, UK Long Gilt and US 10yr T-Note
Trade Indices, stocks and bonds from a single screen
Leverage upto 1:20
| Bonds Name | Country | Symbol | Min Price Fluctuation |
Spread as low as | Avg Spread | Min/Max Trade Size |
Margin % | Contract Size | Profit Currency | Limit/Stop levels |
Trading Hrs - GMT +2 |
|---|

Bonds trading hours (GMT+2 time zone, please note DST may apply)
Monday – Friday: 00:05 – 23:50
For futures CFDs, there is no daily swap charges
Stop/Limit Order levels may vary during news or unusual market conditions without prior notice
The average spreads indicated here are calculated throughout the day. They tend to be narrower under normal market conditions. However, spreads may widen as a result of important news announcements, during political uncertainty, because of unexpected events that can lead to volatile market conditions, or at the close of the business day, or at the weekends when liquidity is lower. During such volatile and illiquid market conditions most liquidity providers quote spreads larger than normal. At such times, spread may increase.
The margin is always calculated using Lager Leg when you Hedge the Positions on CFDs.
The margin requirement for CFDs is calculated like this : Lots x Contract Size x Opening Price x Margin Percentage and not based on the leverage of your trading account.
Frequently Asked Question
Trade the top most FAMOUS BONDS in globe
While a bond’s end return is fixed, the market conditions surrounding its sale can cause fluctuations in its price to buy. High interest rates, for example, tend to make bonds less attractive to investors by providing other means of attaining high returns with low risk. For this reason, interest rates and bond prices tend to have an inverse relationship.
As well as buying bonds during favorable periods, traders can use financial derivatives to speculate on a bond’s market price.
When investing in bonds, choosing a bond that pays in a different currency to your own raises the issue of currency risk. But when trading bonds, you’re free to buy or sell assets from around the world.
Bonds have a clear advantage over other securities and bonds are generally viewed as safer investments than stocks. In addition, bonds do suffer from less day-to-day volatility than stocks, and the interest payments of bonds are sometimes higher than the general level of dividend payments.
The disadvantages of bonds include rising interest rates, market volatility and credit risk. Bond prices rise when rates fall and fall when rates rise. Bond portfolio could suffer market price losses in a rising rate environment.
Investors trade bonds for a number of reasons, with the key two reasons being - profit and protection. Investors can profit by trading bonds to pick up yield (trading up to a higher-yielding bond) or benefit from a credit upgrade (bond price increases following an upgrade).
1. How does bond trading work?
While a bond’s end return is fixed, the market conditions surrounding its sale can cause fluctuations in its price to buy. High interest rates, for example, tend to make bonds less attractive to investors by providing other means of attaining high returns with low risk. For this reason, interest rates and bond prices tend to have an inverse relationship.
As well as buying bonds during favorable periods, traders can use financial derivatives to speculate on a bond’s market price.
2. What is difference between Investing and Trading Bond?
When investing in bonds, choosing a bond that pays in a different currency to your own raises the issue of currency risk. But when trading bonds, you’re free to buy or sell assets from around the world.
3. What are the advantages of trading Bond?
Bonds have a clear advantage over other securities and bonds are generally viewed as safer investments than stocks. In addition, bonds do suffer from less day-to-day volatility than stocks, and the interest payments of bonds are sometimes higher than the general level of dividend payments.
4. What are the disadvantages of trading Bonds?
The disadvantages of bonds include rising interest rates, market volatility and credit risk. Bond prices rise when rates fall and fall when rates rise. Bond portfolio could suffer market price losses in a rising rate environment.
5. What are the two main reasons people buy bonds?
Investors trade bonds for a number of reasons, with the key two reasons being - profit and protection. Investors can profit by trading bonds to pick up yield (trading up to a higher-yielding bond) or benefit from a credit upgrade (bond price increases following an upgrade).
 Home
Home Funds
Funds Partners
Partners Get Help
Get Help FAQ
FAQ Chat With Us
Chat With Us Contact Us
Contact Us Call Back Request
Call Back Request Sign Up
Sign Up Cabinet
Cabinet
 About Us
About Us  Client Protection
Client Protection Account Types
Account Types Funding
Funding Trading Conditions
Trading Conditions Forex
Forex Commodities
Commodities Indices
Indices Cryptos
Cryptos Stocks
Stocks Bonds
Bonds MetaTrader 5
MetaTrader 5 FIX API
FIX API New to Forex
New to Forex Forex Glossary
Forex Glossary Traits of Successful Traders
Traits of Successful Traders Articles
Articles Ebooks
Ebooks Trading Strategies
Trading Strategies Daily Forecast
Daily Forecast Market Insights
Market Insights Weekly Forecast
Weekly Forecast Live charts
Live charts Economic Calendar
Economic Calendar Market Sentiment
Market Sentiment